1. Functionalism
The Bauhaus placed a strong emphasis on functionality. It aimed to create designs and objects that served practical purposes and met the needs of everyday life. The movement sought to integrate art and design with industrial production, focusing on the utilitarian aspects of objects and buildings.
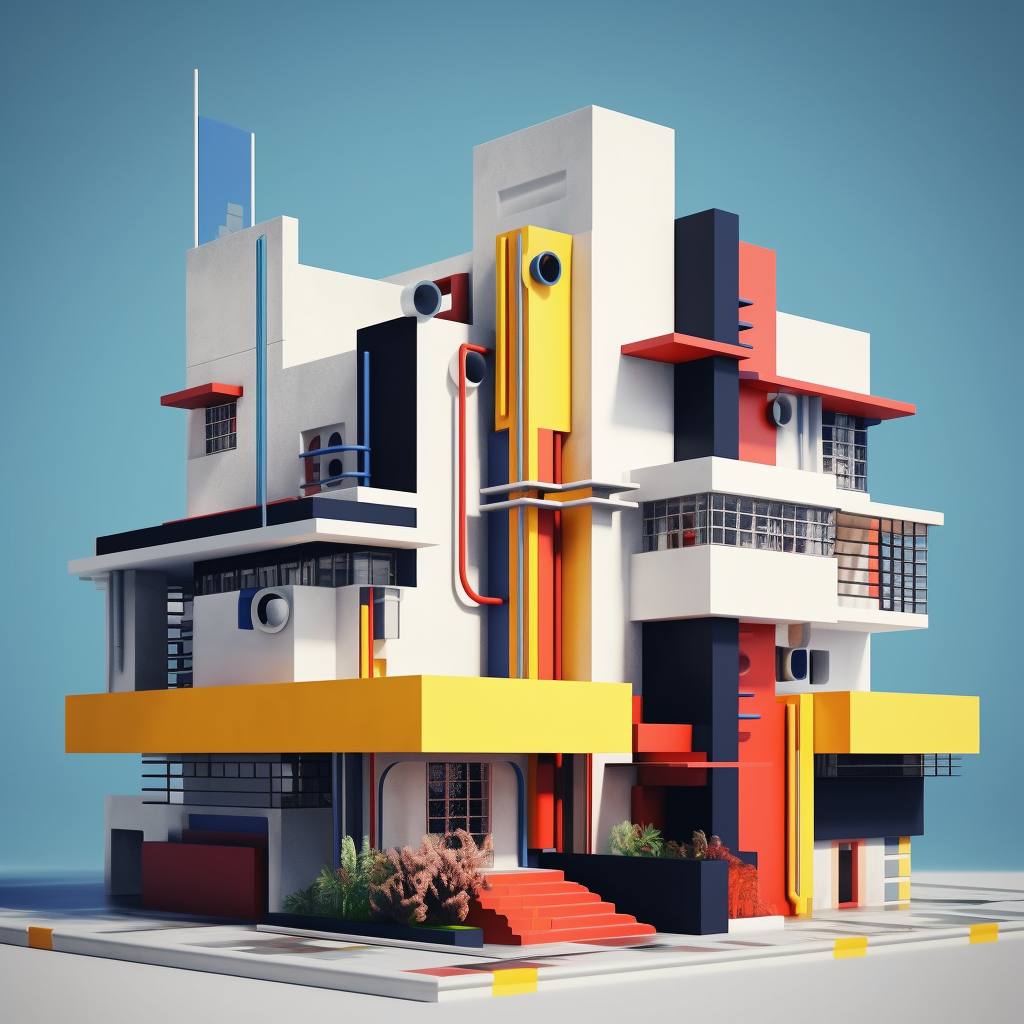
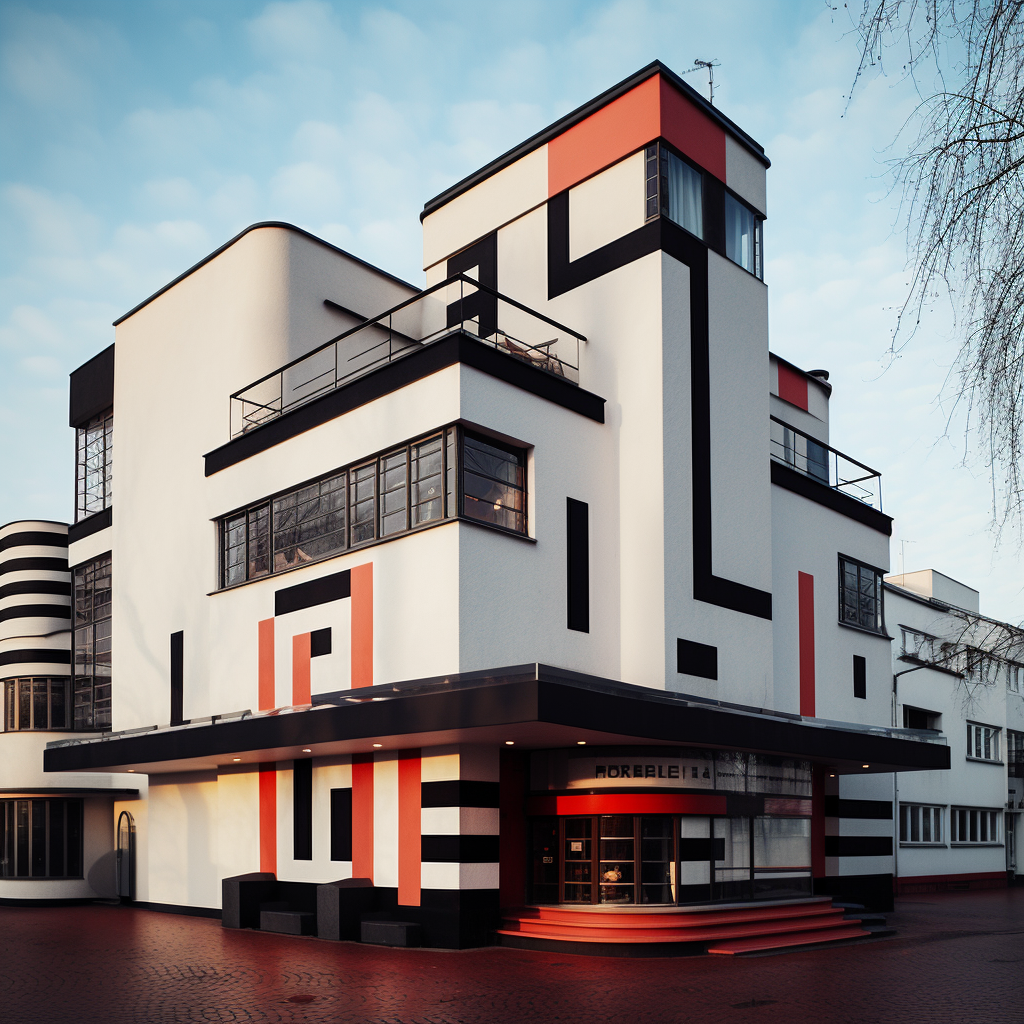
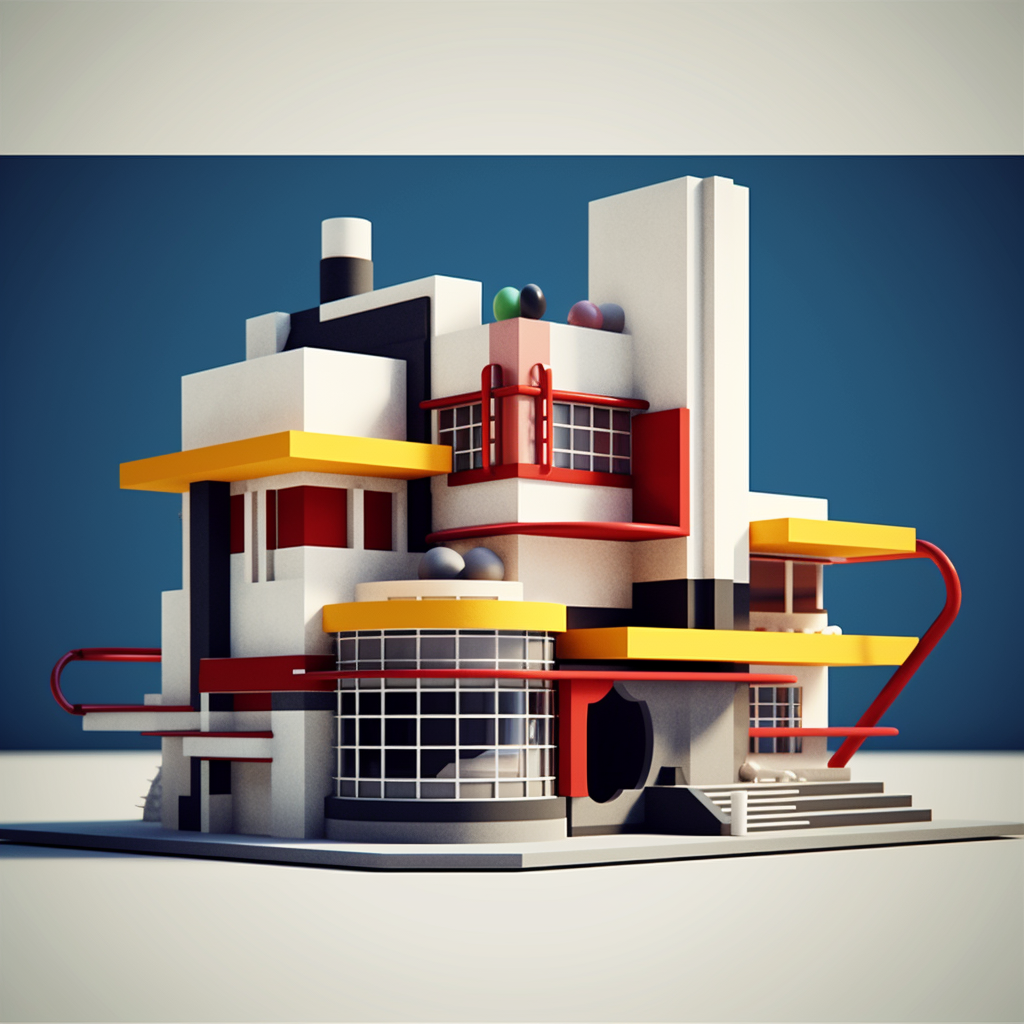
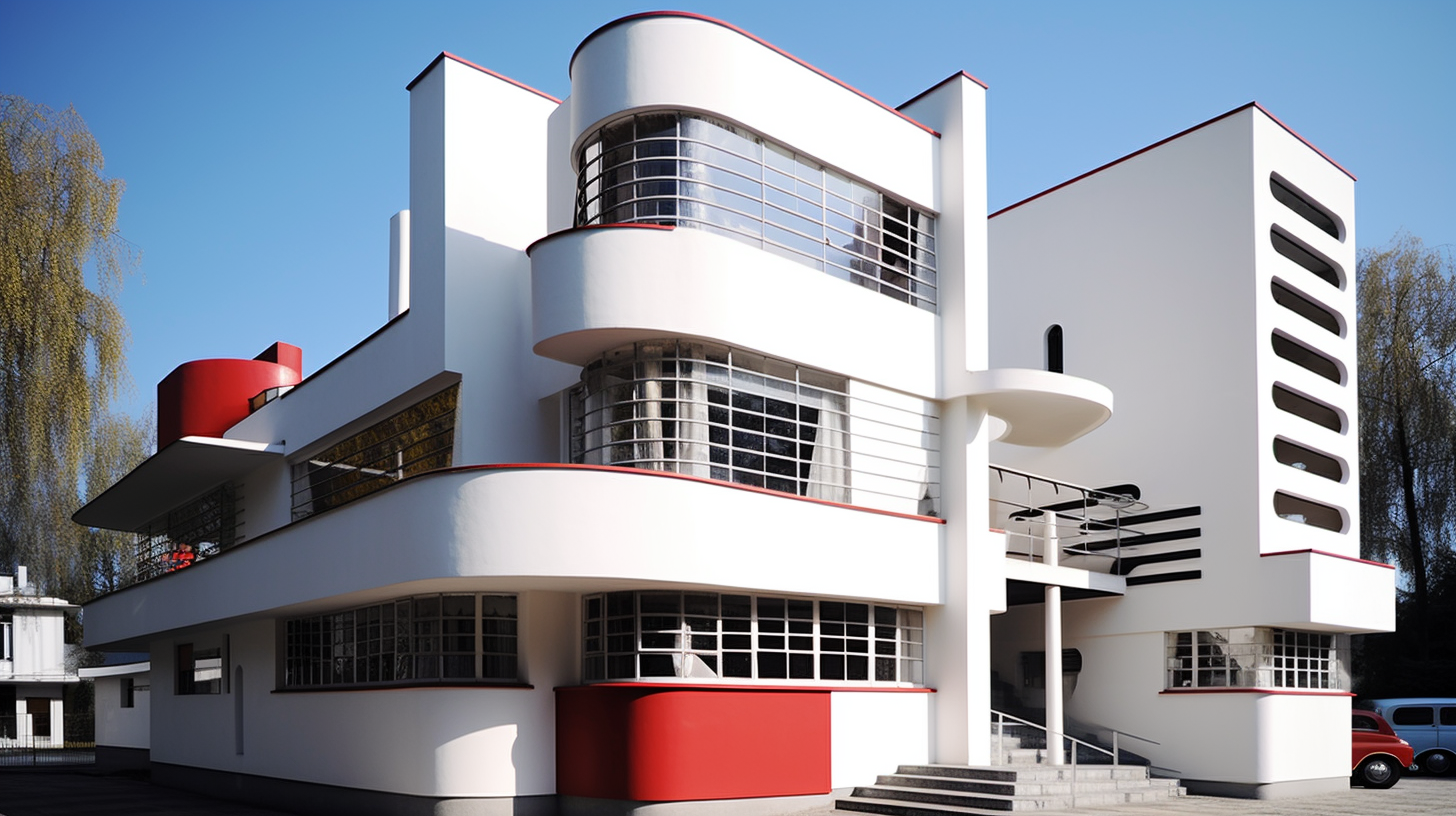








2. Minimalism and Simplicity
Bauhaus designs often featured clean lines, geometric shapes, and a reduction of ornamentation. The movement rejected excessive decoration and embraced simplicity in form and design. This minimalist approach aimed to achieve visual clarity and efficiency.


3. Integration of Art and Technology:
The Bauhaus embraced the new materials and technologies of the time. It sought to combine traditional craftsmanship with modern industrial processes. Artists and designers at the Bauhaus explored the potential of materials such as steel, glass, and concrete, using them to create innovative and functional designs.





4. Interdisciplinarity
The Bauhaus encouraged collaboration and interdisciplinary work. It brought together artists, architects, designers, and craftsmen from various disciplines. The idea was to create a community where different skills and perspectives could merge and influence one another, fostering a holistic approach to design.
5. Experimentation and Innovation
The Bauhaus fostered an environment of experimentation and innovation. Artists and designers were encouraged to explore new ideas, techniques, and materials. The movement sought to push the boundaries of traditional art and design, challenging established norms and conventions.


6. Total Work of Art (Gesamtkunstwerk)
The Bauhaus aimed to create a total work of art where all elements of design, from architecture to furniture, textiles, and typography, were harmoniously integrated. This holistic approach aimed to create a unified and cohesive aesthetic experience.
7. Accessibility and Mass Production
The Bauhaus sought to make good design accessible to a wider audience. It aimed to bridge the gap between art and the general public by creating functional and affordable designs that could be mass-produced.
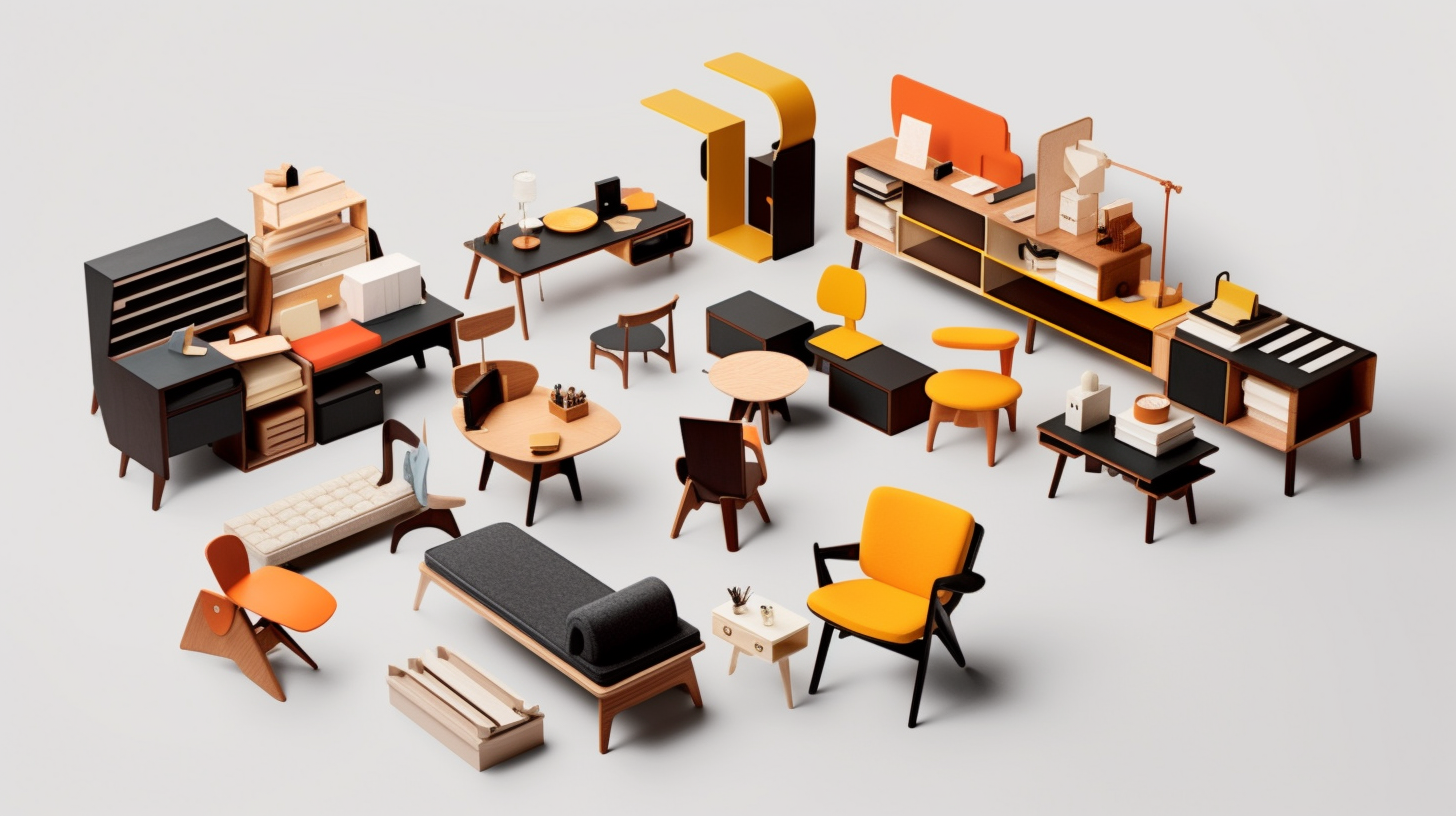
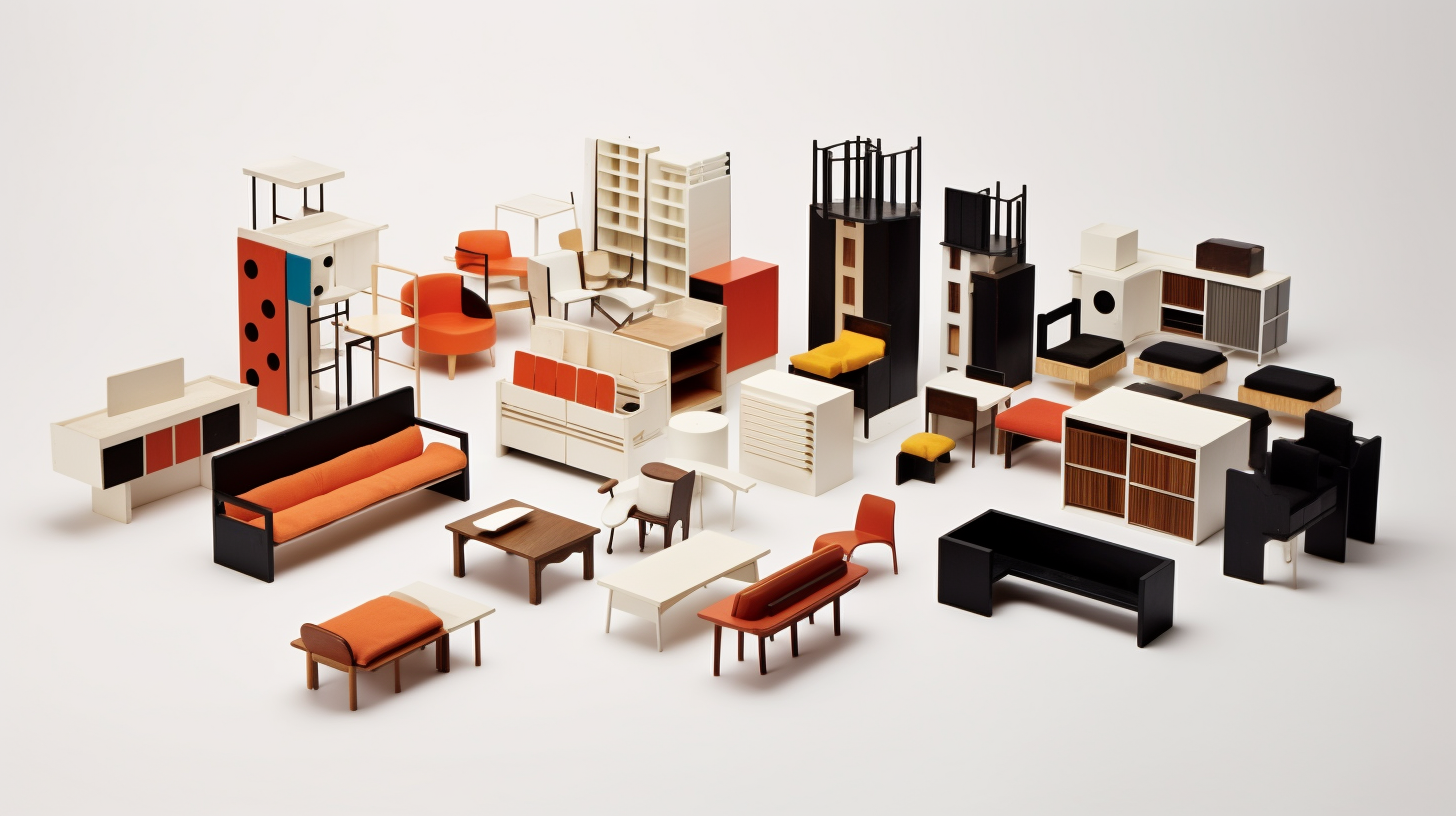
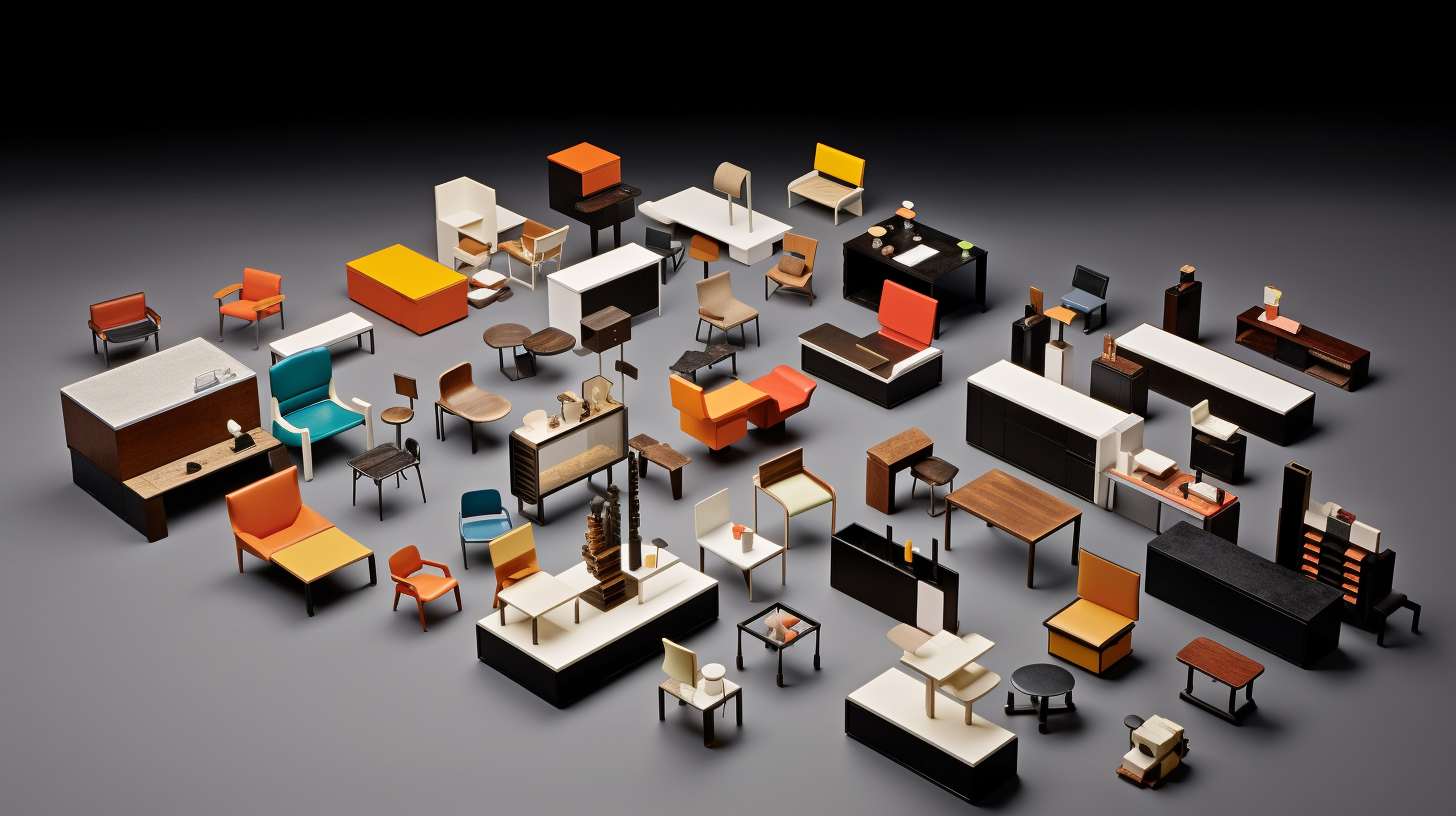



8. Progressive Social and Political Ideals
The Bauhaus movement was driven by a desire for social progress and a belief in the transformative power of design. Many members of the Bauhaus believed that good design could contribute to the betterment of society. The movement aspired to create a new visual language for the modern world.